Sexual Differentiation of the Embryo Is Normally Determined by
Variations in the phenotypic characteristics of the different sexes are determined during development by internal chemical signals. The chromosomal sex of the embryo is established at fertilization.
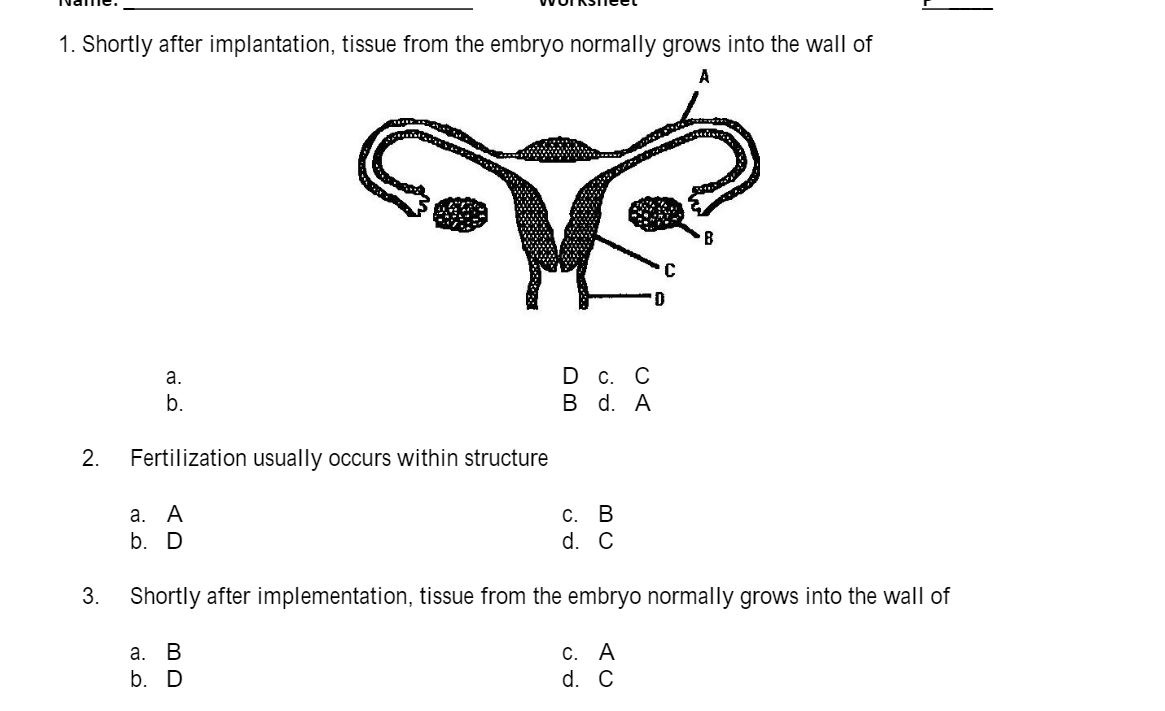
Answered 1 Shortly After Implantation Tissue Bartleby
However 6 weeks elapse in humans before the first signs of sex differentiation are noticed.
. Sexual differentiation occurs subsequently and is controlled by gonadal hormones that act at critical times during organogenesis. Sexual differentiation -Sex determined by chromosomes established at fertilization -Reproductive systems of male and female are identical at early stages of development Location of genes involved in gonadal sex differentiation -The SRY of Y gene codes for production of SRY protein which causes testis differentiation. Prior to this the child is considered bipotential because it cannot be identified as male or female.
Usually refers to differences between the two sexes. Initially we did not know what this factor was and it was designated the testis determining factor TDF. The sex of an early embryo cannot be determined because the reproductive structures do not differentiate until the seventh week.
Three lines of evidence suggest that instead sex determination may start shortly after conception. In all vertebrates the genetic basis of sex is determined by meiosis a process by which paired chromosomes are separated resulting in the formation of an egg or sperm which are then joined at fertilization. Since the female is XX each of her eggs has a single X chromosome.
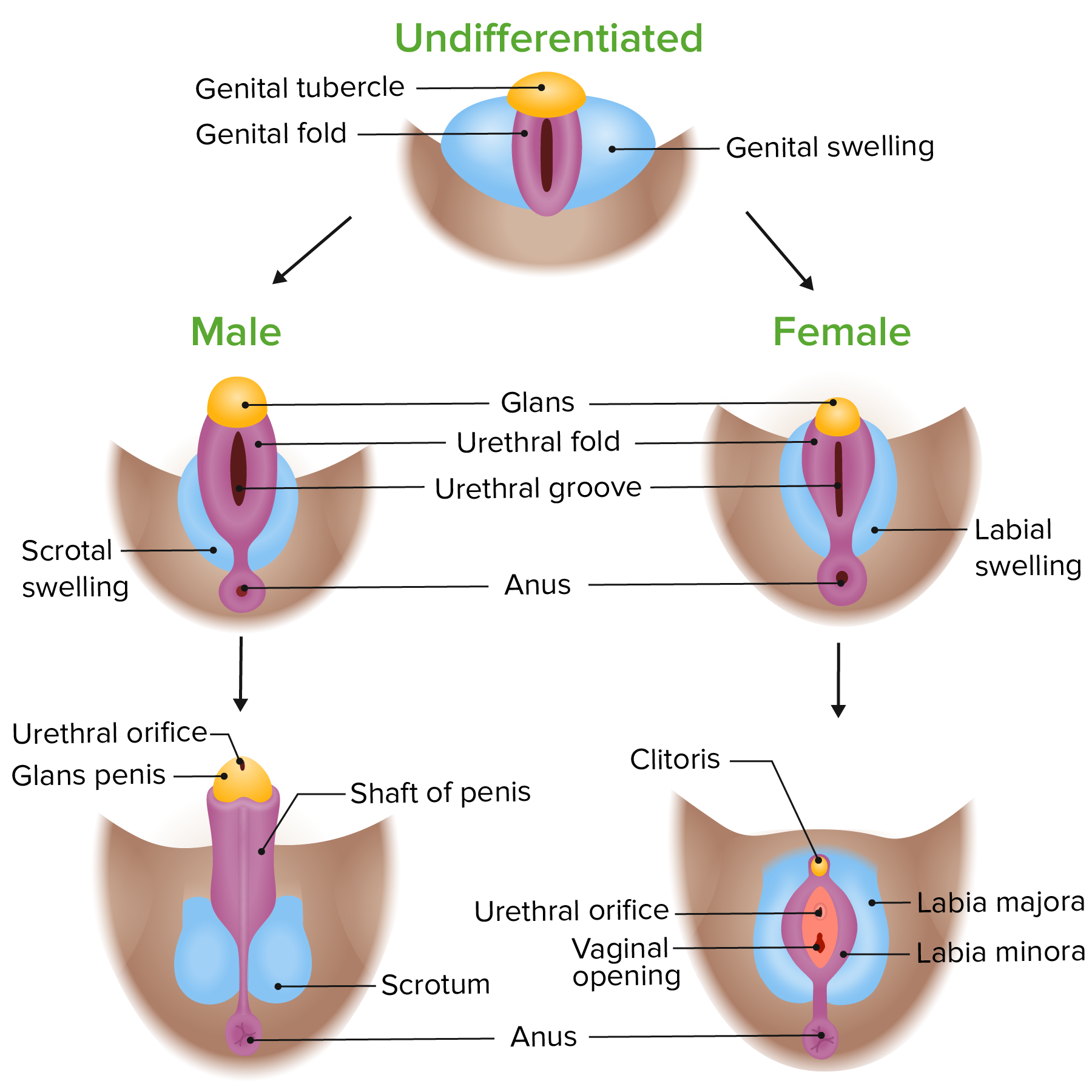
The paired mesonephric ducts Wolffian ducts and paramesonephric ducts Müllerian ducts contribute the majority of male and female internal. Testicular hormones induce masculinization while feminization does not require female hormonal intervention. Sexual differentiation in human embryology the process by which the male and female sexual organs develop from neutral embryonic structures.
Sex differentiation involves a series of events whereby the sexually indifferent gonads and genitalia progressively acquire male or female characteristics. Dimorphic Having two different forms. In the absence of the chromosome gonadal and genital differentiation proceeds along female lines with no proven role for fetal or maternal hormones in this process.
This lecture covers embryonic sexual differentiation covering gonad internal and external genital development. We now know since 1990 that TDF is the protein product encoded by the SRY gene on the Y chromosome. In the presence of chromosomes short arm known as the sex determinant region of the chromosome the embryo and bipotential gonad differentiate into a teste.
Testicular hormones induce masculinization while feminization does not require female hormonal intervention. Differentiation of internal genital organsand ducts - late embryo to fetal 4. Sex differentiation is the development of an undifferentiated gonad and its transformation into either a testis or ovary.
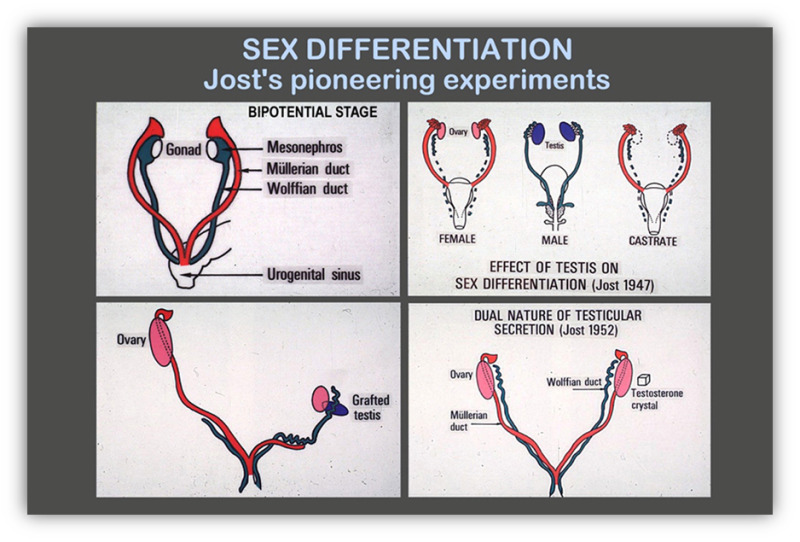
In 1947 Carl Richard Moore a researcher at the University of Chicago in Chicago Illinois wrote Embryonic Sex Differentiation and Sex Hormones which was published in the same year as a first-edition monographIn the book Moore argues that regulation of sex differentiation in mammals is not controlled by sex hormones secreted by embryonic sex organs gonads. Every individual must have at least one X chromosome. Describe gonad differentiation and hormone secretion starting with the SRY gene.
1 the xy preimplantation embryo usually develops more rapidly than the xx preimplantation embryo this phenotype has been linked to the y chromosome and will be termed growth factor y. Sexual differentiation is the process of development of the sex differences between males and females from an undifferentiated zygote. This produces the phenotypic sex on an individual basis and the sex ratio on a population basis.
The SRY gene contains instructions for making the SRY protein which causes the embryo to develop as male. Sex determination is often distinct from sex differentiation sex determination is the designation for the development stage towards either male or female while sex differentiation is the pathway towards the development of the. Development of the indifferent gonad- genital ridge early embryo 2.
Differences in development are dependent on a protein product of the Y chromosome SRY gene. In mammals primary sex determination is strictly chromosomal and is not usually influenced by the environment. The normal human fetus of either sex has the potential to develop either male or female organs depending on genetic and hormonal influences.
They named the region of the Y chromosome that contains the TDF the sex-determining region Y or the SRY gene because the presence of that specific region of the Y chromosome determines an embryos biological sex. Differentiation of external genitalia- fetal 5. Inside the cells the chromosomes determine whether the embryo will develop into a male or a female.
In humans sex is determined by the constitution sex chromosomes in first and the second week of gestation where the embryos of both the sexes differ only in their karyotype-males are XY and females are XX. Primary sex determination is the determination of the gonads. 1 SRY gene causes the PRIMORDIAL GONAD to become the testes.
The axiom of mammalian reproduction is that a 46XX embryo will differentiate into a female and a 46XY embryo becomes a male. Stages of Sexual Differentiation 1. Sexual differentiation the process by which individuals develop the characteristics associated with being male or NEfLeSmOaNle and KRIEGSFELD sex determination The point at which an individual begins to develop as either a male or a female.
The ovum donates one X chromosome and the sperm donates either one X or one Y chromosome. Sexual differentiation occurs subsequently and is controlled by gonadal hormones that act at critical times during organogenesis. The two sets of ducts are the Wolffian ducts which eventually become the male vas deferens epididymis on the testes and seminal vesicles and the Müllerian ducts which eventually become the oviducts uterus and vagina.
Differentiation of gonad - testis or ovary late embryo defining event in sexual differentiation 3. 2 TESTES secrete TESTOSTERONE and ANTI-MULLERIAN HORMONE. Sexual Differentiation Genetic sex is determined at the time of fertilization.
In most cases the female is XX and the male is XY. Sexual Differentiation Genetic sex is determined at the time of fertilization. In the third week of gestation specific genes induce differentiation of gonads.
2 the gene for testis determination srysry and the. Sex determination malefemale at the biological level is determined by the presence or absence of the Y chromosome. 3a Anti-mullerian hormone causes the mullerian duct female to.
Sex differentiation in fish is highly dependent on steroid hormones the androgens and estrogens.

Sexual Differentiation Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

Sexual Differentiation Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
Comments
Post a Comment